i really like your site its very nice information.
IS HIIT the Most Effective & Efficient Fat Loss Exercise Program?
June 02 2008
It is pretty well established that exercise alone (without any dietary intervention) does a poor job in losing weight. Dietary intervention or diet has been shown to be significantly more effective in losing weight than just exercise alone. But what about HIIT or interval training? Is interval training or HIIT more effective & efficient in losing weight than regular cardio?
What was the purpose of the HIIT study?
Most exercise programs for weight loss consist of some sort of cardiovascular activity at a moderate, steady-state intensity for around 30 - 45 minutes. In this recent study, the researchers compared the current exercise guidelines for weight loss with an exercise protocol which involves brief, high-intensity exercise followed by brief slightly longer low intensity exercise (HIIT or interval training).
This type of high intensity intermittent training (HIIT) is popularly known as Interval Training. An earlier study had shown HIIT/interval training to be more effective than regular steady state cardio, but the study involved 45 min of exercise, 5 times a week which could be highly demanding for sedentary overweight individuals. Hence the researchers opted for a less demanding version of the same HIIT program:
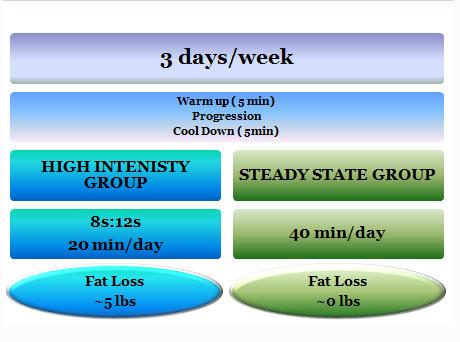
Figure: Summary of the HIIT study
What was the HIIT study design?
There were two exercise groups (HIIT & Steady State) and a control.
High Intermittent intensity training (HIIT) protocol:Each subject performed 8 s of sprinting and 12 s of turning the pedals slowly for 20 - 30 rpm for a maximum of 60 repeats of sessions. The subjects started out with .5 kg resistance and worked as hard as they could during the 8 sec sprint. Subjects started with as little as 5 min of conditioning phase and gradually increased it to a maximum of 20 min. Once an individual could complete the 20 min at .5 kg resistance or the heart rate decreased due to increased fitness, the resistance was increased by increments of .5 kg.
Steady state exercise (SSE) Protocol:The subjects exercised at 60% of the Vo2 peak. Subjects started the program at his intensity for 10-20 minutes and gradually increased it to a maximum of 40 min of exercise per session.
The points to remember are both groups (HIIT & Steady State) maintained their workload as their fitness improved by increasing the resistance, both had a warm up and cool down session, and both raised their workload and time in a progressive manner.
What were the HIIT study results?
Interestingly, despite exercising half the time, HIIT subjects lost 11.2% fat ( about 5 lbs) whereas the SSE subjects experienced no fat loss! Mind you, it’s only 5 lbs in 15 weeks which still shows the ineffectiveness of exercise alone in losing weight.
That been said, 5 lbs is a significant amount if you scan the relevant scientific literature. According to the 2006 Cochrane review on exercise, the average weight loss was 1-1.5 ( 3lbs) with a follow up between 3-12 months. The study do note the presence of responders and non responders: participants who were the leanest lost the least amount. If you take out the non- responders, the mean fat loss was much greater, around 8 lbs.
Both protocols decreased fasting insulin levels (measure of insulin resistance), but the effect was significantly greater for HIIT compared to SSE.
What are the potential mechanisms of HIIT?
Notably, Total Energy expenditure for both groups remained pretty similar. So how did the HIIT report greater fat loss compared to SSE?
The researchers assume that the changes in HIIT may have been influenced by underreported changes in diet. As other studies have shown, HIIT may have suppressed appetite or decreased attraction to energy rich foods. Another explanation is that this type of intense exercise may result in increased fat utilization for the HIIT group.
Anyhow, atleast this study does shows that high intensity intermittent training (HIIT) is more effective & efficient than steady state cardio to keep your body fat in check.